LC 00797: verschil tussen versies
Geen bewerkingssamenvatting |
k (Tekst vervangen - "reason of being" door "reason for existence") |
||
| (9 tussenliggende versies door een andere gebruiker niet weergegeven) | |||
| Regel 1: | Regel 1: | ||
Mutual understanding and shared meaning are key notions in the Social Theory (ST). Unfortunately, they are also confusing notions because understanding and meaning are closely related and often regarded as synonyms. A precise meaning (or understanding for that matter) can be given in the realm of | Mutual understanding and shared meaning are key notions in the {{Internal link|link=LC 00346|name=Social Theory (ST)|dialog=process-linkpage-dialog}}. Unfortunately, they are also confusing notions because understanding and meaning are closely related and often regarded as synonyms. A precise meaning (or understanding for that matter) can be given in the realm of {{Internal link|link=LC 00479|name=SSM's PQR formula|dialog=process-linkpage-dialog}} and {{Internal link|link=LC 00511|name=EMont|dialog=process-linkpage-dialog}}. | ||
The goal of gaining mutual understanding in a Social Innovation (SI) process is to recognize and acknowledge stakeholders' worldviews in order to create room for movement.[[Bestand:Worldview PQR v 20221002.png|gecentreerd|miniatuur| | The goal of gaining mutual understanding in a Social Innovation (SI) process is to recognize and acknowledge stakeholders' worldviews in order to create room for movement. A stakeholder's worldview can be captured with the PQR formula in terms of what and why (P-R, reason for existence), and how (Q's, particular ways of doing things). The PQR formula, possibly augmented with EM<sub>ont</sub>'s beliefs and conditions, explicates a worldview of a stakeholder so that other stakeholders can comprehend it.[[Bestand:Worldview PQR v 20221002.png|gecentreerd|miniatuur|322x322px|Worldview in terms of PQR.]]Recognizing and acknowledging a particular worldview, however, is not the same as attaching the same meaning or importance to it by others. Almost by definition, worldviews will clash in wicked problems. A SI process to establish mutual understanding opens the door to understanding the positions taken by stakeholders, which might lead to common grounds in the sense of shared meaning. That is, the SI process helps to find shared meaning, but it cannot in itself guarantee that a shared meaning is actually established. As a bare minimum, stakeholders can agree to disagree by realizing that they need each other in order to make progress. [[Bestand:Shared meaning PQR v 20221002.png|gecentreerd|miniatuur|644x644px|Shared meaning in terms of PQR.]]It is important to note that the overarching P-system and R-system are notional constructs that do not necessarily exist in any tangible form by the stakeholders. It can be seen as an unspoken pact shared by all stakeholders. In case of shared meaning is found, it can be explicated by defining the overarching P-system and R-system as the reason for existence of the system. Somehow the P's and R's of individual stakeholders (in this figure a and b) should then be traceable to the overall P-system and R-system. | ||
[[Bestand:Shared meaning PQR v 20221002.png|gecentreerd|miniatuur|644x644px|Shared meaning in terms of PQR.]] | |||
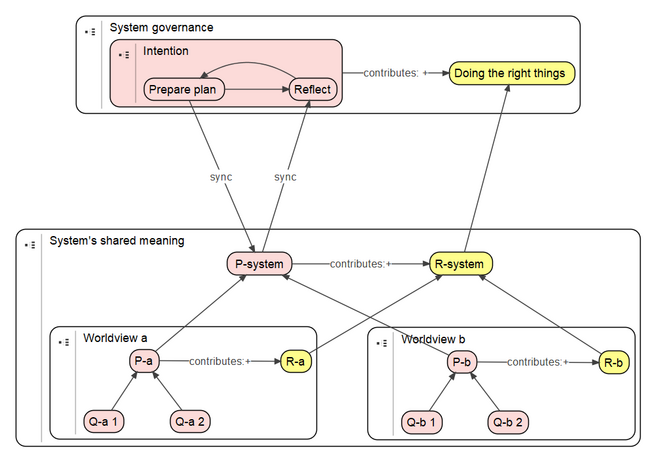
[[Bestand:System governance v 20221020.png|gecentreerd|miniatuur|657x657px|System governance in terms of PQR.]] | If stakeholders see the benefit of having a common ground, i.e., a shared meaning, they can actively facilitate each other in such a way that the sum of the whole is greater than the parts (1 + 1 > 2). It might be the case that some stakeholders have to change their practices (see the section on {{Internal link|link=LC 00555|name=Exploring Change|dialog=process-linkpage-dialog}}). This can also lead to emerging properties in the whole. That is, conditions (indicators) can be associated with R-system that are measures of some properties that cannot be traced back to properties of individuals. | ||
One step further is to make P-system and R-system tangible entities by including them in a governance structure that steers, monitors and adapt the behavior of individual stakeholders by setting the right conditions. This can take all kind of forms, for instance, by establishing rules of conduct or installing more regulative procedures to grant or revoke rights and financial means.[[Bestand:System governance v 20221020.png|gecentreerd|miniatuur|657x657px|System governance in terms of PQR.]] | |||
{{LC Book config}} | {{LC Book config}} | ||
Huidige versie van 29 apr 2023 om 11:45
Mutual understanding and shared meaning are key notions in the Social Theory (ST). Unfortunately, they are also confusing notions because understanding and meaning are closely related and often regarded as synonyms. A precise meaning (or understanding for that matter) can be given in the realm of SSM's PQR formula and EMont.
The goal of gaining mutual understanding in a Social Innovation (SI) process is to recognize and acknowledge stakeholders' worldviews in order to create room for movement. A stakeholder's worldview can be captured with the PQR formula in terms of what and why (P-R, reason for existence), and how (Q's, particular ways of doing things). The PQR formula, possibly augmented with EMont's beliefs and conditions, explicates a worldview of a stakeholder so that other stakeholders can comprehend it.
Recognizing and acknowledging a particular worldview, however, is not the same as attaching the same meaning or importance to it by others. Almost by definition, worldviews will clash in wicked problems. A SI process to establish mutual understanding opens the door to understanding the positions taken by stakeholders, which might lead to common grounds in the sense of shared meaning. That is, the SI process helps to find shared meaning, but it cannot in itself guarantee that a shared meaning is actually established. As a bare minimum, stakeholders can agree to disagree by realizing that they need each other in order to make progress.
It is important to note that the overarching P-system and R-system are notional constructs that do not necessarily exist in any tangible form by the stakeholders. It can be seen as an unspoken pact shared by all stakeholders. In case of shared meaning is found, it can be explicated by defining the overarching P-system and R-system as the reason for existence of the system. Somehow the P's and R's of individual stakeholders (in this figure a and b) should then be traceable to the overall P-system and R-system.
If stakeholders see the benefit of having a common ground, i.e., a shared meaning, they can actively facilitate each other in such a way that the sum of the whole is greater than the parts (1 + 1 > 2). It might be the case that some stakeholders have to change their practices (see the section on Exploring Change). This can also lead to emerging properties in the whole. That is, conditions (indicators) can be associated with R-system that are measures of some properties that cannot be traced back to properties of individuals.
One step further is to make P-system and R-system tangible entities by including them in a governance structure that steers, monitors and adapt the behavior of individual stakeholders by setting the right conditions. This can take all kind of forms, for instance, by establishing rules of conduct or installing more regulative procedures to grant or revoke rights and financial means.
- Lees hiervoor:
- Lees hierna: